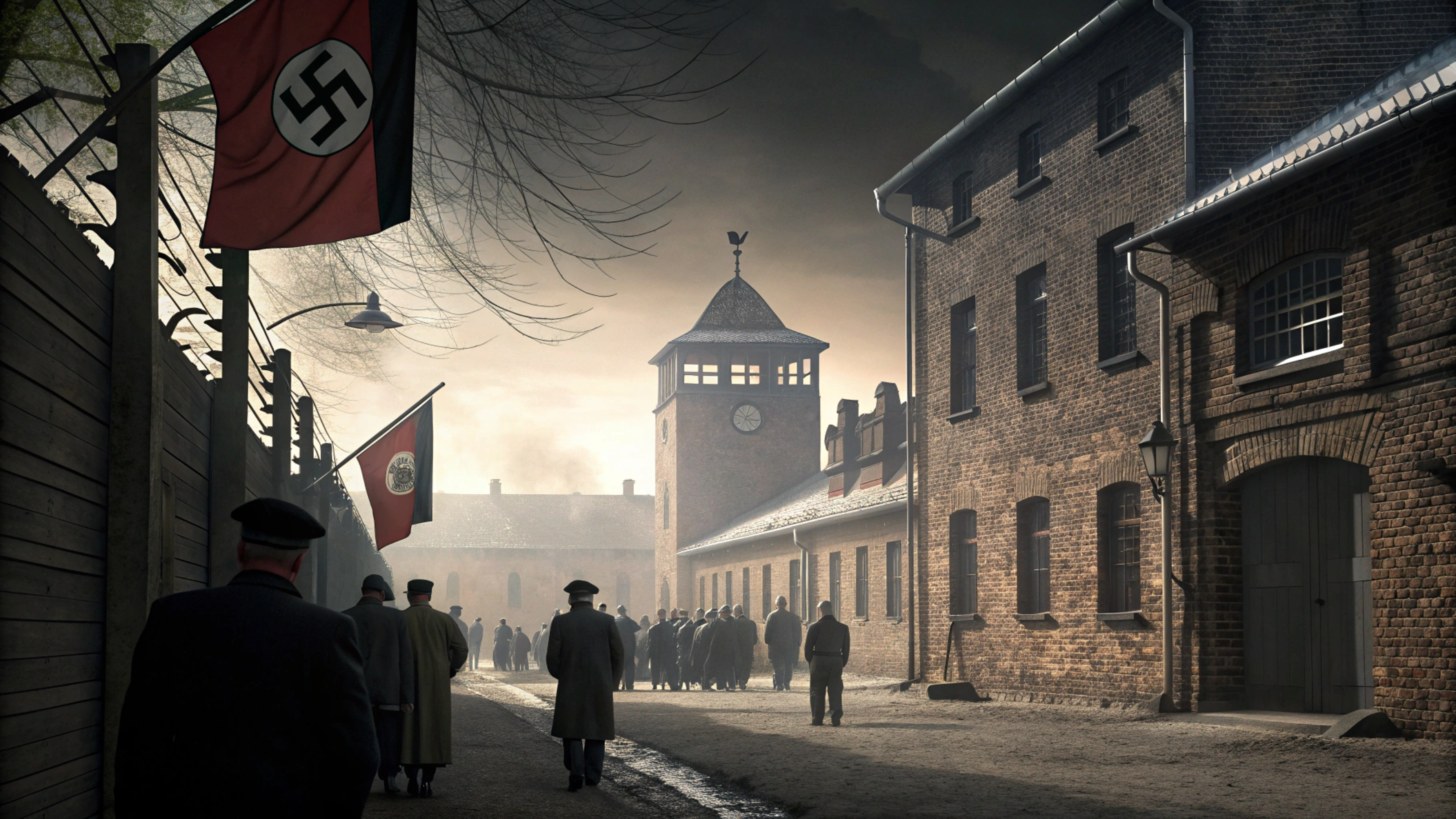
Fascisterne
The term fascisterne is the Danish word for “the fascists” and refers to individuals and groups who embrace or embody fascist ideologies. Rooted in a history marked by national upheaval and radical political change, fascisterne exemplifies a political philosophy and movement that has left a lasting mark on world history. Understanding who the fascisterne are and what they represent is essential to comprehending the complex social, cultural, and political dynamics in Europe and beyond.
What Does Fascisterne Mean?
Fascisterne directly translates to “the fascists” in Danish and points to followers of fascism, a political ideology characterized by:
- Strong authoritarian leadership and centralized government control.
- Intense nationalism combined with a belief in the supremacy of one nation or race.
- Suppression of political dissent and opposition.
- Rigid social and economic regimentation.
- Often, militarism and propaganda are used to enforce conformity.
At its core, it represent those who support or act according to these principles. The term is linked to historical regimes that emerged primarily in Europe during the early to mid-20th century, particularly Mussolini’s Italy and later Nazi Germany.
Historical Context: The Rise of Fascisterne in Europe
Fascism, which gave rise to it, emerged from the turmoil following World War I. The post-war period was marked by deep economic crises, political instability, and social unrest. Many nations faced crippling debts, unemployment, and fears about communism.
In Italy, Benito Mussolini galvanized support with his promise of national revitalization through strong, decisive leadership. Similarly, Adolf Hitler in Germany exploited widespread resentment toward the Treaty of Versailles, promoting a racially charged nationalist vision.
Fascisterne groups spread across several European countries, offering authoritarian solutions amid chaos. Their ideology appealed to those disillusioned with democratic institutions and economic hardship but ultimately led to devastating conflicts and human rights abuses.
Key Characteristics of Fascisterne
Understanding the defining features of fascisterne helps explain both their appeal and dangers:
- Extreme Nationalism: It emphasizes a collective national identity, often excluding or vilifying minorities and outsiders.
- Authoritarian Rule: They advocate for a centralized, autocratic government, dismissing individual freedoms for the sake of state power.
- Militarism: The glorification of military strength and readiness for conflict is a hallmark.
- Suppression of Dissent: Fascisterne regimes use propaganda, censorship, and violence to eliminate opposition.
- Racism and Xenophobia: Many fascisterne believe in racial superiority and enforce discriminatory policies.
Influential Figures Among the Fascisterne
Some of the most notorious historical figures associated with it ideology include:
- Benito Mussolini: The founder of Italian Fascism, Mussolini established the first fascist state and influenced others worldwide.
- Adolf Hitler: The German dictator whose Nazi regime represented an extreme form of fascism, leading to World War II and the Holocaust.
- Giovanni Gentile: An intellectual who provided philosophical underpinnings for fascist doctrines, emphasizing the supremacy of the state over the individual.
These leaders shaped not only their nations but global political history, and their legacies serve as tragic warnings.
The Legacy and Impact of Fascisterne
Though World War II ended the reign of the most infamous fascist regimes, it left profound scars on societies. Their ideology caused devastating wars, genocide, and the erosion of democratic values.
Today, the legacy of it informs many discussions about nationalism, authoritarianism, and the dangers of extreme political movements. The resurgence of some nationalist and authoritarian tendencies worldwide has renewed interest and concern about the ideology’s potential to disrupt peace and equality.
Lessons from Fascisterne for Today’s World
Understanding fascisterne is more than a historical exercise; it is essential for recognizing and combating echoes of fascist ideology in modern politics. Key takeaways include:
- Vigilance against authoritarian tendencies.
- Promoting pluralism and protecting minority rights.
- Educating about the historical consequences of intolerance.
- Encouraging democratic participation and dialogue.
Conclusion
Fascisterne, or “the fascists,” represent a political philosophy with deep historical roots and lasting effects on society. Their emphasis on authoritarianism, nationalism, and suppression of dissent presents enduring challenges and warnings for contemporary politics. Understanding their origin, ideology, and impact helps us safeguard democratic values and build inclusive societies.
Visit Inter-net-chicks.com